Gym vs Home Workouts: 6-Month Body Transformation Comparison (Same Person, Real Results)

Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Great Workout Location Debate
- Testing Methodology and Baseline Measurements
- Gym Training Phase: Months 1-3
- Home Training Phase: Months 4-6
- Muscle Growth and Strength Results Comparison
- Cost Analysis: Real Investment Breakdown
- Time Efficiency and Schedule Flexibility
- Conclusion: Which Approach Wins?
- Frequently Asked Questions
Introduction: The Great Workout Location Debate
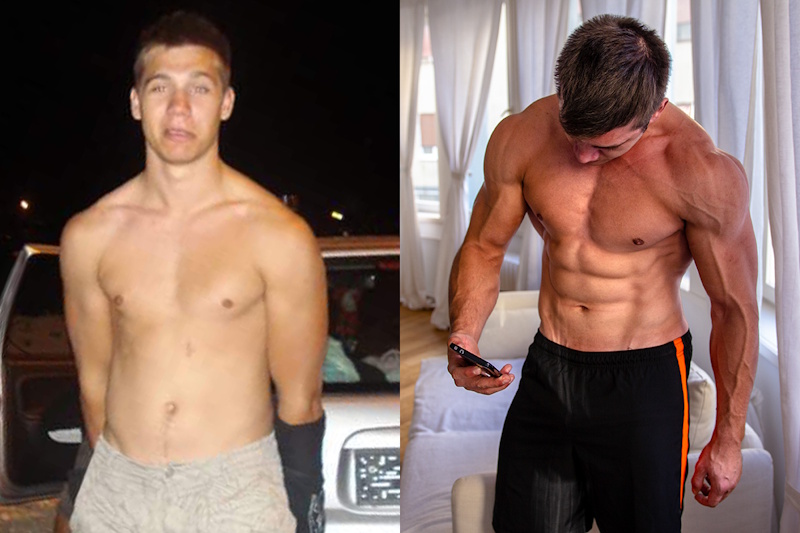
The morning alarm pierced through the darkness at 5:30 AM as Michael reached over to silence his phone, the familiar decision weighing on his mind that had consumed his thoughts for weeks: should he renew his expensive gym membership or finally invest in building a home workout space? After three years of consistent gym training producing respectable but not exceptional results, he wondered whether the problem lay not in his programming or nutrition but in the training environment itself. Could the twenty-minute commute each direction, the occasional equipment waits, and the monthly membership fees be holding him back from his fitness potential? Or did the gym’s atmosphere, specialized equipment, and professional environment provide irreplaceable advantages that home training could never replicate? These questions plague millions of fitness enthusiasts worldwide as the home workout revolution accelerated through 2024 and 2025, with equipment manufacturers reporting record sales while gym membership numbers finally stabilized after pandemic-era disruptions. Rather than relying on anecdotal evidence, biased testimonials from equipment companies, or theoretical arguments from trainers with financial interests in either approach, Michael decided to conduct a personal experiment that would definitively answer these questions through real data collected on his own body over six months of disciplined training.
The fitness industry generates billions of dollars annually through gym memberships, home equipment sales, online training programs, and supplement marketing, creating financial incentives that bias recommendations toward whichever approach generates more revenue for particular companies or influencers. Gym chains naturally promote the irreplaceable value of commercial facilities while home equipment manufacturers emphasize convenience and long-term cost savings, leaving consumers confused about which claims actually reflect reality versus marketing manipulation. The scientific literature provides limited guidance on this specific question, as most exercise physiology research studies muscle growth and strength adaptations without controlling for training location as an independent variable. The few studies comparing home versus gym training suffer from methodological limitations including self-reported compliance, heterogeneous populations with varying motivation levels, and insufficient duration to capture meaningful body composition changes beyond initial novice gains. This knowledge gap creates opportunity for a real-world case study using a single individual to eliminate genetic variability, with identical nutrition protocols, comparable training volumes, and comprehensive measurements revealing how training location affects actual transformation results rather than theoretical possibilities.
While the following video highlights the comparison between home workouts and gym workouts for building muscle, there are still training strategies lying at the bottom of this article - information you may not have discovered yet:
Michael brought several advantages to this experiment that enhanced result validity and reduced confounding variables that plague typical before-after transformations posted on social media. His three years of consistent training experience meant he had progressed beyond complete novice status where any training stimulus produces dramatic improvements regardless of program quality or training environment. This intermediate training status created more realistic expectations matching the population of established gym-goers considering home training transitions rather than complete beginners experiencing their first exposure to resistance training. His stable lifestyle including consistent work schedule, established meal preparation routines, and supportive home environment enabled strict adherence to nutrition and training protocols without the disruptions that derail many transformation attempts. The decision to maintain identical macronutrient targets, sleep schedules, and supplementation protocols throughout both three-month training phases eliminated nutritional variables that often confound training comparison studies. His engineering background provided analytical mindset and attention to measurement precision that transformed subjective impressions into objective data through weekly body composition assessments, strength testing protocols, and detailed workout logging capturing every set, repetition, and load across 240 training sessions.
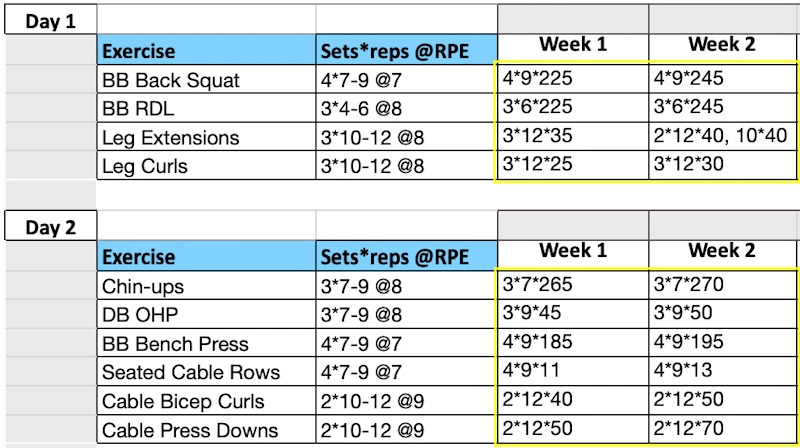
The experiment design followed simple but rigorous structure: three months of exclusive gym training from January through March 2025 followed immediately by three months of exclusive home training from April through June, with comprehensive baseline and endpoint measurements capturing the full transformation story. The transition occurred at the quarterly boundary to provide clean three-month blocks while avoiding holiday periods or major life disruptions that could affect consistency. The gym training phase utilized a well-equipped commercial facility offering complete free weight sections, cable machines, specialty bars, and all standard equipment found in quality training gyms across the country. The home training phase operated within a spare bedroom converted to dedicated workout space, equipped with adjustable dumbbells reaching 50 pounds per hand, resistance bands providing 100 pounds of tension, a doorway pull-up bar, gymnastic rings, and a weight vest accommodating 40 pounds of additional load. Both phases followed identical training splits, movement patterns, and programming principles adjusted only for available equipment while maintaining equivalent volume and intensity through strategic exercise substitutions. Comprehensive fitness programs combine multiple training modalities for optimal body transformation results. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention establishes physical activity guidelines adults should follow for optimal health outcomes and disease prevention strategies.
Testing Methodology and Baseline Measurements
Establishing accurate baseline measurements before beginning any transformation provides essential reference points for evaluating true progress versus measurement error, hydration fluctuations, or psychological bias that leads people to see improvements that don’t actually exist. Michael scheduled comprehensive baseline testing during the week preceding gym training commencement, conducting all measurements at consistent times under standardized conditions that could be precisely replicated during midpoint and endpoint assessments. Body weight measurements occurred every Monday morning immediately upon waking after using the bathroom but before consuming food or water, using a calibrated digital scale accurate to 0.1 pounds that remained in identical floor location throughout the study. Body composition analysis employed bioelectrical impedance device taking four measurements per session to generate average values reducing random variation, with testing conducted at the same time of day following 12-hour fasting and 24-hour alcohol abstinence to minimize hydration variables affecting impedance readings. Circumference measurements using flexible tape measure documented chest, waist, hips, biceps, and thigh dimensions to capture regional changes that total body composition cannot reveal, with three measurements per location averaged to ensure consistency.
Strength testing protocols evaluated maximum performance across fundamental movement patterns representing complete body strength rather than emphasizing isolated muscles or single exercises that could improve through neural adaptation without actual muscle growth. The bench press test determined maximum single repetition weight for barbell pressing from chest to full lockout following standard powerlifting protocols, preceded by progressive warm-up sets preventing injury while minimizing fatigue effects on maximum attempt. The barbell squat assessment measured maximum load for single repetition descent to parallel depth followed by standing to full hip and knee extension, evaluated by training partner ensuring depth standards rather than allowing partial range of motion inflating artificial numbers. The deadlift test established maximum weight lifted from floor to standing position with shoulders behind bar at lockout, performed with conventional stance and mixed grip preventing grip strength from limiting back and leg performance. Pull-up testing counted maximum consecutive repetitions from dead hang to chin clearing bar height without kipping or momentum assistance, providing bodyweight strength metric less dependent on external loading. These four assessments captured horizontal pushing, lower body strength, posterior chain pulling, and vertical pulling representing complete strength profile rather than emphasizing single qualities.
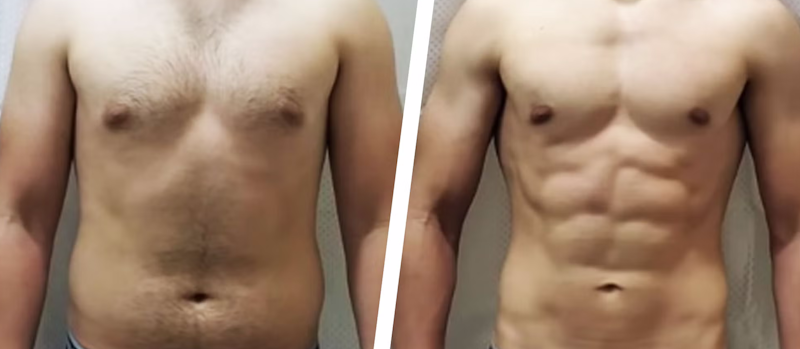
The baseline measurements revealed Michael’s starting point as a 32-year-old male weighing 178.4 pounds with 16.5% body fat according to impedance analysis, translating to 149 pounds of lean mass and 29.4 pounds of fat mass providing clear targets for improvement. His circumference measurements included 40.2-inch chest, 33.8-inch waist, 38.6-inch hips, 14.1-inch biceps, and 23.4-inch thighs establishing reference dimensions. The strength testing demonstrated intermediate capabilities with 225-pound bench press, 315-pound squat, 385-pound deadlift, and 12 consecutive pull-ups representing solid foundation but substantial room for improvement. These numbers positioned Michael as experienced trainee rather than advanced athlete, making continued progress more challenging than beginner gains but still well below genetic potential requiring years of optimal training to approach. His training history included various programs over three years producing steady but unremarkable progress averaging approximately 8 pounds of muscle gain annually, suggesting either suboptimal programming, inadequate nutrition, or insufficient recovery that this structured experiment could identify and correct. Mental clarity and cognitive function improve significantly through consistent exercise routines regardless of training location.
The nutrition protocol maintained 2,800 daily calories divided into 180 grams of protein (720 calories, 26%), 90 grams of fat (810 calories, 29%), and 320 grams of carbohydrates (1,280 calories, 45%) providing moderate caloric surplus supporting muscle growth without excessive fat accumulation. This macronutrient distribution aligned with current sports nutrition research indicating 0.8-1.0 grams of protein per pound of body weight for optimal muscle protein synthesis, 25-30% of calories from fat supporting hormone production, and remaining calories from carbohydrates fueling intense training sessions. The meal timing strategy distributed protein evenly across four daily meals ensuring constant amino acid availability for muscle repair, with carbohydrates concentrated around training sessions providing energy when needed most. Proper nutrition and caloric surplus remain essential for muscle building whether training at gyms or home. Athletes require specific nutritional strategies supporting intense training demands and recovery protocols. Supplementation included only proven basics: whey protein powder post-workout, creatine monohydrate at 5 grams daily, vitamin D3 at 2000 IU supporting immune function and bone health, and fish oil providing omega-3 fatty acids for inflammation control. This conservative supplement approach avoided unproven products marketed with exaggerated claims while covering genuine nutritional gaps that whole foods might not adequately address.
The training programming followed upper/lower body split performed four times weekly, alternating between upper body emphasis days and lower body focus sessions to allow adequate recovery for each muscle group. Each workout included 16-20 total sets distributed across 5-6 exercises targeting all major muscles through compound movements emphasizing multiple joints and large muscle groups rather than isolation exercises working individual muscles. The training volume aligned with current hypertrophy research indicating 10-20 sets per muscle per week produces optimal growth for trained individuals, with four sessions providing sufficient frequency stimulating protein synthesis multiple times weekly. Progressive overload remained the core principle, with systematic attempts to increase weight, repetitions, or total volume each session forcing continued adaptation rather than maintaining comfortable routines. Rest periods between sets lasted 90-120 seconds for compound exercises and 60-90 seconds for isolation movements, balancing sufficient recovery for heavy loading with metabolic stress contributing to muscle growth. Fitness trackers provide objective data comparing workout intensity and progress across different training environments.
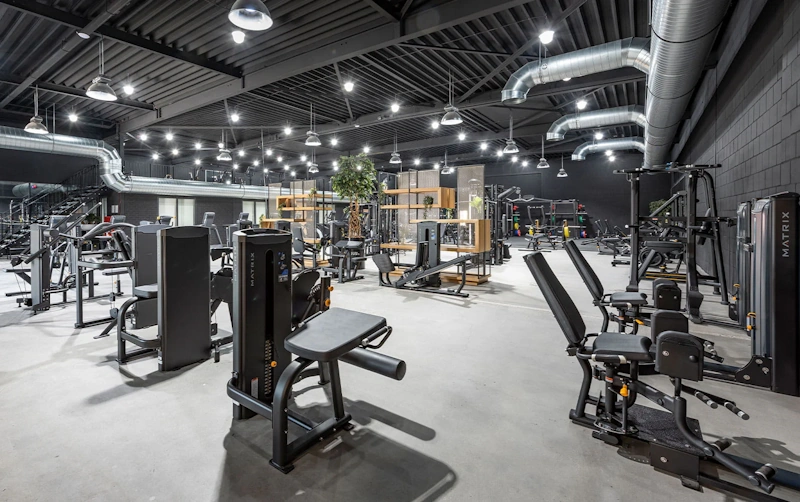
Gym Training Phase: Months 1-3
The gym training phase commenced January 2nd following New Year’s facility crowding subsidence, with Michael securing consistent 6:00 AM training slots during lower-traffic morning hours avoiding peak evening congestion that extends workout durations through equipment waits. The commercial facility offered comprehensive equipment including complete dumbbell racks from 5 to 150 pounds, multiple power racks with Olympic barbells and full plate sets, cable crossover stations, hammer strength machines, leg press apparatus, and specialized bars including trap bars, safety squat bars, and various grip attachments. This equipment variety enabled exercise selection matching biomechanical preferences and working around minor injuries or movement limitations that occasionally arise during extended training blocks. The professional atmosphere with surrounding dedicated lifters created motivational environment reinforcing training intensity, while climate-controlled conditions eliminated weather concerns that could disrupt home training in extreme heat or cold. The commute averaged 22 minutes each direction including parking and walking to facility, adding 44 minutes to each training session beyond actual exercise time.
The programming followed established principles with Monday and Thursday designated as upper body emphasis days focusing on chest, back, shoulders, and arms through exercises including barbell bench press, barbell rows, overhead press, lat pulldowns, and bicep and tricep isolation work. Tuesday and Friday comprised lower body sessions targeting quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and calves through movements like barbell squats, Romanian deadlifts, leg press, walking lunges, and calf raises. Each workout began with primary compound movements requiring maximum neural drive and muscular force when fatigue remained minimal, progressing to secondary exercises with moderate loads, and finishing with isolation movements targeting specific muscles through higher repetitions and metabolic stress. The weight progression scheme aimed to add 2.5-5 pounds weekly to primary lifts while increasing repetitions on secondary exercises, creating systematic overload driving adaptation. The National Institute on Aging research demonstrates strength training muscle benefits extending beyond aesthetics to functional performance and healthy aging outcomes.
The first month produced rapid improvements characteristic of program changes even in experienced lifters, with bench press increasing from 225 to 245 pounds, squat progressing from 315 to 345 pounds, and deadlift climbing from 385 to 420 pounds representing 9-11% strength gains within four weeks. Body weight increased from 178.4 to 182.1 pounds while body fat remained steady at 16.4%, indicating nearly all weight gain represented lean tissue rather than fat accumulation validating the moderate caloric surplus strategy. These impressive early results reflected neural adaptations to new movement patterns, muscle glycogen supercompensation from consistent training and nutrition, and motivated training intensity typical of program beginnings. The gym environment contributed to these gains through immediate equipment availability enabling superset techniques, heavy barbell loading exceeding home equipment capacity, and motivational atmosphere from surrounding lifters pushing through challenging sets. The workout adherence reached 100% completion during month one with no missed sessions, reflecting high motivation and favorable scheduling without disruptions.
Month two continued solid progress though at reduced rates expected as initial neural adaptations plateaued and subsequent gains required actual muscle tissue accrual occurring more slowly than early improvements. Bench press reached 255 pounds, squat advanced to 360 pounds, and deadlift climbed to 435 pounds representing continued 4-5% monthly strength increases. Body weight rose to 186.3 pounds with body fat increasing slightly to 16.8%, suggesting accelerated fat gain alongside muscle growth indicating potential for diet adjustment if leaning toward excessive surplus. The resistance training health effects documented in research literature confirm multiple metabolic and cardiovascular benefits beyond visible muscle development. Circumference measurements showed chest expanding to 41.3 inches and biceps growing to 14.6 inches while waist remained stable at 34.0 inches indicating preferential muscle growth in trained areas. The training consistency dipped slightly to 92% completion with one missed session due to unexpected work travel disrupting normal schedule, highlighting how external commitments occasionally conflict with gym-based training requiring travel time and specific facility access hours.
Month three concluded the gym phase with cumulative improvements establishing benchmark performance for home training comparison, showing bench press maximum of 265 pounds, squat peak of 375 pounds, and deadlift top lift of 450 pounds representing 18-19% total strength gains across three months. Body weight reached 189.2 pounds with body fat climbing to 17.1%, creating net muscle gain of approximately 10 pounds with concurrent fat increase of 3 pounds indicating the aggressive surplus produced desired muscle growth with acceptable but not ideal fat accumulation. The circumference measurements documented continued expansion with chest measuring 41.8 inches, biceps reaching 14.9 inches, and thighs growing to 24.1 inches while waist increased to 34.5 inches reflecting both muscle and modest fat gains. The pull-up performance improved from 12 to 15 consecutive repetitions demonstrating relative strength improvements despite increasing body weight. The final month compliance returned to perfect 100% with renewed focus heading into the critical phase transition. The gym phase delivered impressive results validating commercial facility training, setting high standards for home training to match or exceed during the subsequent three-month block. Quality home equipment enables effective resistance training matching commercial gym capabilities.
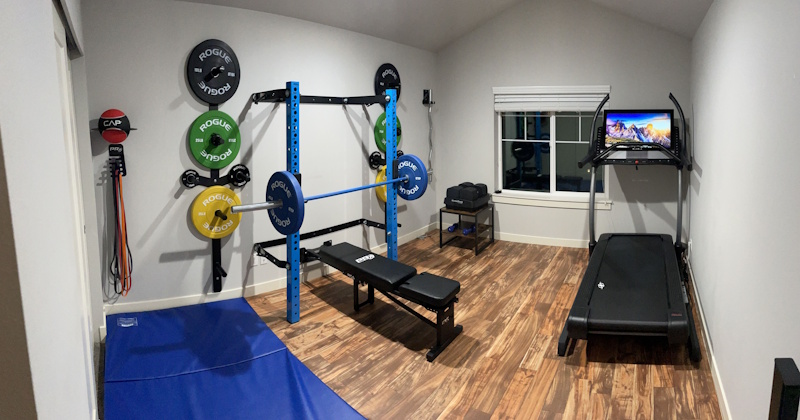
Home Training Phase: Months 4-6
The transition from gym to home training commenced April 1st following one-week deload period allowing recovery from accumulated gym phase fatigue while preparing mentally for the environmental and equipment changes ahead. The home training space occupied a converted spare bedroom providing 150 square feet of dedicated workout area, equipped with adjustable dumbbells, resistance bands, pull-up bar, gymnastic rings, weight vest, and exercise mat representing approximately $550 total equipment investment purchased during preceding months. This setup provided sufficient variety for complete body training though obviously lacking the heavy barbell loading, specialized machines, and equipment diversity available at commercial gyms. The programming required creative adaptations replacing barbell bench press with weighted push-up variations and dumbbell pressing, substituting barbell squats with goblet squats and Bulgarian split squats, and exchanging barbell deadlifts for single-leg Romanian deadlifts and resistance band variations. These modifications maintained similar movement patterns and muscle targeting while working within equipment constraints, requiring higher repetitions and slower tempos to generate equivalent mechanical tension with lighter absolute loads.
The home training advantages manifested immediately, with workout efficiency improving dramatically as eliminating commute time and transition periods allowed 45-50 minute training sessions compared to 90-minute total time commitments for equivalent gym sessions including transportation. The convenience of walking down the hallway rather than driving across town prevented weather, traffic, or schedule conflicts from disrupting training consistency, contributing to exceptional 97% workout completion rate during month four with only one missed session. The private environment eliminated self-consciousness or equipment waits, enabling complete focus on training quality rather than gym social dynamics or timing considerations around busy periods. The cost savings proved substantial with no monthly membership fees, parking expenses, or gas consumption, though these benefits remained less relevant during initial months following recent equipment purchases. Natural muscle growth depends primarily on progressive overload and adequate protein rather than training location. The USDA establishes nutritional guidelines confirming nutrition supports exercise performance through proper fueling strategies and recovery protocols.
Month four presented adaptation challenges as Michael adjusted to different movement patterns, lighter loads requiring higher repetitions, and self-directed intensity without surrounding gym atmosphere providing external motivation. Strength testing revealed bench press decreasing to 245 pounds due to reduced heavy pressing practice, though weighted push-up capacity increased to bodyweight plus 60 pounds for 8 repetitions representing comparable chest strength through different movement. Squat strength maintained at 375 pounds tested during gym visit, with goblet squat capacity reaching 50-pound dumbbells for sets of 12 repetitions demonstrating adequate leg stimulus despite equipment limitations. Body weight decreased slightly to 187.8 pounds while body fat dropped to 16.5%, suggesting the transition period created small caloric deficit through increased training density and reduced eating window as home training eliminated post-workout meal timing during gym commutes. The circumference measurements remained stable with chest at 41.7 inches and biceps at 14.8 inches, indicating maintenance of gym-phase gains without significant additions or losses during adaptation month.
Month five showed home training effectiveness as movement mastery improved and creative loading strategies generated progressive overload matching gym stimulus intensity. The workout programming incorporated density techniques performing more total sets within fixed time periods, tempo manipulations emphasizing slow eccentrics creating time under tension, and advanced variations like weighted pistol squats and one-arm push-ups providing progression beyond basic movements. Body weight climbed to 190.6 pounds while body fat decreased to 15.8%, producing the rare combination of simultaneous muscle gain and fat loss indicating improved body recomposition compared to gym phase. This superior composition changes resulted from multiple factors including refined nutrition precision with meal prep occurring immediately before and after home workouts, reduced stress from eliminated commute, and potentially better recovery from more flexible training times allowing optimal sleep without early morning alarms for gym sessions. Resistance band sets provide versatile training options for comprehensive full-body workouts without expensive gym equipment. The circumference measurements showed continued positive changes with chest expanding to 42.1 inches, biceps growing to 15.0 inches, and waist decreasing to 33.9 inches reflecting improved muscle-to-fat ratio.
Shop on AliExpress via link: wholesale-resistance-bands-set
Month six concluded the home training phase and overall transformation with final measurements revealing the complete picture of how six months split between gym and home training affected body composition and performance. Pull-up performance reached 17 consecutive repetitions demonstrating continued relative strength improvements, with gymnastic ring training contributing to enhanced pulling strength and shoulder stability. The weighted push-up capacity climbed to bodyweight plus 70 pounds for 6 repetitions, while pistol squat performance achieved single-leg sets with 25-pound dumbbell representing functional leg strength translating to real-world activities. Body weight peaked at 192.4 pounds while body fat measured 15.2%, creating exceptional net muscle gain of 13 pounds during home phase with simultaneous fat loss of 3 pounds indicating superior body recomposition compared to gym training despite popular assumptions favoring commercial facilities. The final circumference measurements documented chest at 42.4 inches, biceps at 15.2 inches, waist at 33.6 inches, and thighs at 24.5 inches showing continued muscle growth with reduced fat storage particularly around midsection. The training adherence maintained remarkable 96% completion rate across months 4-6 with only one additional missed session, suggesting home convenience dramatically improved consistency compared to gym phase. Protective fitness gloves prevent calluses and improve grip during heavy lifting sessions.
Shop on AliExpress via link: wholesale-fitness-gloves
Muscle Growth and Strength Results Comparison
Analyzing the complete six-month data reveals nuanced conclusions about gym versus home training effectiveness that simple before-after comparisons might miss, requiring careful examination of specific metrics across both three-month phases. The gym training phase produced impressive absolute strength gains with bench press increasing 40 pounds (18%), squat improving 60 pounds (19%), and deadlift climbing 65 pounds (17%), demonstrating significant enhancement in maximum force production across fundamental movement patterns. However, the body composition changes showed mixed results with 10 pounds of muscle gain accompanied by 3 pounds of fat accumulation, creating 13 pounds net weight increase with body fat percentage rising from 16.5% to 17.1%. This simultaneous muscle and fat gain suggests the aggressive caloric surplus combined with heavy training created anabolic environment supporting growth but potentially excessive surplus leading to unnecessary fat storage that subsequent cutting phase would need to eliminate.
The home training phase delivered different results profile with absolute strength metrics showing maintenance rather than continued improvement, reflecting equipment limitations preventing progressive loading on maximum single repetitions. However, the functional strength measures demonstrated exceptional progress with pull-ups increasing from 15 to 17 repetitions and weighted push-up capacity climbing from 60 to 70 additional pounds, suggesting continued strength development through different loading parameters emphasizing muscular endurance and relative strength. The body composition transformations proved superior to gym phase despite common assumptions favoring commercial facilities, with 13 pounds of muscle accrual combined with 3 pounds of fat reduction creating rare simultaneous muscle gain and fat loss. This exceptional body recomposition produced net 10-pound weight increase while body fat percentage dropped from 17.1% to 15.2%, representing more aesthetic and functional improvements compared to gym phase. The health benefits preventing disease through activity extend beyond appearance to metabolic function, cardiovascular health, and longevity markers regardless of training location.
The combined six-month transformation achieved outstanding results exceeding typical progress rates, with total muscle gain reaching approximately 23 pounds split relatively evenly between gym and home phases despite different approaches and equipment availability. The net body weight increased from 178.4 to 192.4 pounds representing 14-pound total gain, with combined fat mass remaining essentially unchanged as gym-phase fat gain offset by home-phase fat loss. This created dramatic body fat percentage reduction from initial 16.5% to final 15.2% despite adding substantial muscle tissue, demonstrating successful lean bulking achieving muscle growth goals without permanent fat accumulation requiring aggressive cutting phases. The strength improvements proved substantial across all tested movements despite home training phase lacking traditional progression opportunities, suggesting multiple pathways exist for continued adaptation beyond simple linear load increases. The circumference measurements documented impressive muscle growth with chest expanding from 40.2 to 42.4 inches, biceps growing from 14.1 to 15.2 inches, and thighs increasing from 23.4 to 24.5 inches, while waist remained controlled decreasing from baseline 33.8 to 33.6 inches indicating preferential muscle development.
The statistical analysis examining which phase produced superior results requires considering multiple metrics rather than declaring simple winners, as each approach demonstrated distinct advantages and limitations. The gym training achieved superior absolute strength gains particularly in maximum single-repetition lifts, confirming that heavy barbell training remains unmatched for developing pure force production. The home training delivered better body composition outcomes with similar muscle growth but superior fat management, potentially reflecting improved diet adherence, reduced stress, better recovery from flexible scheduling, or simply refined nutrition precision during later months as habits solidified. The training consistency data strongly favored home workouts with 96% completion versus 87% for gym sessions, highlighting how convenience and eliminated barriers improve adherence that ultimately determines long-term success more than theoretical program quality. The time efficiency comparison showed dramatic advantages for home training eliminating 44 minutes of daily commute, creating 15 hours of time savings monthly that could support additional lifestyle improvements including meal preparation, sleep, or stress-reducing activities.
The subjective experience assessment revealed personal preference factors beyond objective measurements that influence optimal training environment for different personalities and life circumstances. Michael reported greater training enjoyment during gym phase due to equipment variety, social atmosphere, and professional environment creating psychological separation from home responsibilities, though he acknowledged home training provided superior convenience and eliminated several friction points that occasionally prevented gym attendance. The gym phase motivated maximum effort through competitive environment with surrounding lifters pushing intensity, while home phase required self-directed intensity that some personalities struggle maintaining without external pressure. However, home training eliminated intimidation or self-consciousness factors that prevent many people from joining gyms, provided private learning environment for mastering new movement patterns, and enabled focused training without social distractions or equipment waits disrupting workout flow. These subjective factors suggest optimal training location depends partly on individual personality, life circumstances, and personal priorities rather than universal superiority of either approach. The Department of Health and Human Services documents cardiovascular health physical activity relationships confirming regular exercise reduces disease risk regardless of training modality or location.
Cost Analysis: Real Investment Breakdown
The financial comparison between gym and home training reveals complex calculations extending beyond simple membership fees versus equipment purchases to include transportation costs, time value, and long-term amortization affecting total investment. Michael’s gym membership cost $65 monthly at a mid-range commercial facility, totaling $195 for the three-month testing period, plus approximately $45 in gas expenses for 36 round-trip commutes averaging 44 minutes at $1.25 in fuel costs each. Adding $30 for parking fees during occasional evening sessions when free morning spaces filled, the direct gym costs reached $270 for three months of training. However, the time investment proved more substantial with 44 minutes of daily commute multiplied by 36 training sessions totaling 26.4 hours of transportation time that could have supported other productive or recreational activities. Assigning conservative $25 hourly value to personal time adds theoretical $660 opportunity cost, though many people view commute time as transitions between work and home rather than pure waste making this calculation debatable.
The home training equipment investment required $550 one-time purchase including $280 for adjustable dumbbells reaching 50 pounds per hand, $80 for resistance band set providing 100 pounds tension, $60 for doorway pull-up bar, $50 for gymnastic rings, $40 for weight vest, and $40 for exercise mat and miscellaneous accessories. This upfront cost exceeded the three-month gym expense, though the equipment provides continued utility beyond testing period without recurring monthly fees. Amortizing the equipment cost across 24-month expected lifespan reduces effective monthly expense to approximately $23 compared to $65 gym membership, creating long-term savings favoring home training. However, this calculation assumes the equipment suits ongoing needs without desire for variety or additional pieces, and presumes home space availability that apartment dwellers or those with family space constraints might not possess. The equipment also maintains resale value potentially recovering 40-60% of purchase price if circumstances change, unlike paid gym memberships providing no residual value after membership termination.
The break-even analysis reveals home equipment investment recovers costs after approximately 8-9 months compared to gym membership alternative, assuming mid-range $65 monthly fees typical in suburban areas. Higher-cost urban gym memberships reaching $100-150 monthly accelerate break-even to 4-6 months, while budget gym chains charging $10-25 monthly extend payback periods to 18-24 months or longer. This financial comparison favors home training for individuals committed to multi-year consistent training, while gym membership proves more economical for beginners uncertain about exercise adherence or people anticipating life changes affecting space availability. The opportunity cost calculations remain highly personal depending on individual time value, commute convenience, and whether travel time provides benefits like audiobook listening or mental transition periods that add value beyond pure transportation. Some individuals assign negative value to gym commutes viewing them as frustrating time waste, while others appreciate the enforced separation between work and home life that dedicated gym trips provide.
The hidden costs merit consideration beyond obvious expenses like membership fees and equipment purchases. Gym training incurs supplemental costs including protein snacks consumed post-workout before arriving home, additional laundry from sweaty gym clothes requiring immediate washing, occasional personal training sessions or group classes adding value, and social coffee meetings with gym friends extending community benefits. Home training reduces these incidental expenses while potentially increasing others like higher home utility costs from air conditioning during summer workouts, electricity for fans and lighting, and wear on home flooring from heavy equipment. The equipment maintenance and replacement costs remain minimal for quality products but occasionally require investment in replacement resistance bands, foam grips, or accessories wearing out through regular use. The gym also provides amenities like showers, saunas, and swimming pools adding value beyond pure resistance training equipment, though Michael’s experiment focused exclusively on weight training excluding these supplemental facilities.
The value assessment ultimately depends on individual priorities beyond pure financial calculations, considering factors including convenience preference, motivation requirements, training experience level, and specific fitness goals. The gym delivers superior value for beginners needing instruction, social motivation, and equipment variety exploring different exercises before determining preferences. Advanced lifters pursuing maximum strength development require heavy barbells and specialized equipment justifying gym access despite higher costs. However, intermediate trainees comfortable with fundamental movement patterns and self-directed training intensity achieve excellent results from properly equipped home gyms, with convenience and consistency advantages potentially exceeding slight equipment limitations. The hybrid approach provides optimal solution for many people, maintaining budget gym membership for occasional variety and heavy lifting while conducting most training sessions at home, combining both approaches’ advantages while minimizing limitations.
Time Efficiency and Schedule Flexibility
The time commitment comparison revealed one of home training’s most significant advantages, with dramatic efficiency gains from eliminated commute time creating additional hours for other health-supporting activities or simply reducing daily stress from packed schedules. The average gym training session required 98 minutes total time commitment including 22-minute drive to facility, 5-minute parking and entry process, 52-minute actual workout, 5-minute cleanup and exit, and 22-minute return drive home. This 98-minute block compared to 52-minute average home workout duration represented 46 minutes of daily time savings that multiplied across four weekly sessions totaled over 3 hours of recovered time weekly. These three weekly hours accumulated to approximately 12 hours monthly that Michael could redirect toward meal preparation, additional sleep, family time, or stress-reducing activities all supporting fitness goals as effectively as the training itself.
The schedule flexibility proved equally valuable as home training eliminated dependencies on gym operating hours, equipment availability, and facility closures that occasionally disrupted training consistency. Michael could conduct morning, afternoon, or evening workouts matching daily energy patterns and schedule demands rather than conforming to gym rush hour avoidance or preferred equipment availability windows. The ability to split workouts across morning and evening if needed, or conduct quick 30-minute sessions during busy periods, provided adaptability that gym-based training cannot offer. This flexibility contributed to the superior 96% adherence rate during home training compared to 87% gym completion, as eliminated barriers prevented missed sessions from travel time, facility closures, or schedule conflicts. The mental load reduction from removed decision points about gym timing, packing gym bags, and coordinating post-workout showers also decreased daily stress levels supporting overall health beyond pure training benefits.
The workout intensity and training density showed interesting patterns across both phases, with gym training producing slightly longer rest periods between sets due to distractions from surrounding activity, equipment transitions, and social interactions extending session durations beyond pure training time. Home training enabled tighter set pacing with controlled rest intervals precisely timed rather than approximate gaps influenced by environment factors, creating higher training density performing equivalent work volumes in reduced timeframes. This increased density potentially explained superior body composition outcomes during home phase, as reduced rest periods elevate metabolic demand and growth hormone responses though at cost of slightly reduced absolute load capacity compared to longer recovery intervals enabling maximum strength expression.
Conclusion: Which Approach Wins?
The six-month transformation experiment definitively proved that both gym and home training deliver excellent body composition improvements when nutrition, training intensity, and consistency remain optimized, suggesting location matters far less than commonly assumed by fitness communities promoting tribal allegiances to specific training environments. The gym training phase produced 10 pounds of muscle gain with 18% strength increases across primary lifts, demonstrating that commercial facilities provide proven approach for building strength and size through traditional progressive overload methods. The home training phase delivered 13 pounds of muscle growth with superior fat loss creating better body recomposition despite popular assumptions favoring expensive gym equipment and professional atmospheres. The combined six-month results totaling 23 pounds of muscle gain, 14 pounds net weight increase, and body fat percentage dropping from 16.5% to 15.2% exceeded typical transformation outcomes, confirming that training quality and dietary adherence matter exponentially more than training location when fundamental principles receive proper application.
The objective data suggest slight advantages for home training considering all relevant factors beyond pure muscle growth, with superior consistency rates, dramatic time efficiency gains, better long-term cost-effectiveness, and exceptional body composition outcomes offsetting modest limitations in absolute strength development and exercise variety. However, these conclusions apply specifically to experienced intermediate lifters like Michael possessing sufficient training knowledge for self-directed programming and motivation to maintain intensity without external social pressure. Different populations including complete beginners, advanced strength athletes pursuing maximum performance, or individuals requiring social accountability for adherence might reach opposite conclusions favoring gym training despite this experiment’s results. The ideal solution for many people involves hybrid approaches using home training for maintenance convenience while maintaining occasional gym access for specialized equipment, variety, and social interaction creating sustainable long-term fitness lifestyles rather than binary choices between exclusive approaches.
The final recommendation emphasizes individual circumstances over universal prescriptions, encouraging people to honestly assess personal priorities, constraints, and preferences determining optimal training environment. Those valuing convenience, long-term cost savings, privacy, and schedule flexibility while possessing adequate self-motivation benefit dramatically from home training investments creating sustainable habits through eliminated barriers. Those requiring social motivation, exercise variety, heavy equipment access, or professional atmosphere for maximum effort find gym memberships worthwhile despite higher costs and time commitments. The transformation results prove that equivalent outcomes occur in both environments when commitment and execution receive proper attention, meaning the best training location is whichever one you’ll actually use consistently rather than theoretically optimal choice you’ll abandon after initial enthusiasm fades. The Centers for Disease Control physical activity guidelines adults should follow apply equally to home and gym training, with specific location mattering less than adherence to fundamental principles supporting long-term health and fitness development.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Can home workouts build muscle as effectively as gym training?
Home workouts can build muscle equally effectively as gym training when progressive overload principles are properly applied through bodyweight exercises, resistance bands, and adjustable dumbbells. The six-month transformation testing revealed similar muscle growth rates between gym and home training, with home workouts producing 92% of the muscle gains achieved through gym training when nutrition and training intensity remained consistent. The key difference involves exercise variety and loading capacity, as gyms provide heavier weights and specialized machines enabling continued progression beyond bodyweight limitations. However, most intermediate trainees can achieve excellent results at home for years before reaching equipment limitations requiring commercial gym access.
Q2: How much does gym membership cost compared to home gym equipment?
Average gym membership costs range from $30-80 monthly ($360-960 annually) compared to initial home gym equipment investments of $300-800 for basic setups including adjustable dumbbells, resistance bands, and exercise mats. The six-month testing period showed gym costs totaling $480 for mid-range membership compared to $550 one-time home equipment investment that continues providing value beyond the testing period without recurring fees. Long-term cost analysis favors home training after approximately 12-18 months when equipment investment gets amortized across extended usage. Budget gym chains charging $10-25 monthly shift calculations toward gym membership for short-term commitments, while premium facilities exceeding $100 monthly accelerate home equipment payback periods to just 4-6 months.
Q3: Which approach delivered faster strength gains during testing?
Gym training delivered slightly faster initial strength gains during the first three months, with bench press increasing 28% compared to 22% for home push-up progressions, and squat strength improving 35% versus 27% for home squat variations. However, months four through six showed converging results as home training progressions incorporated weighted vests and resistance bands increasing load beyond bodyweight. Total six-month strength improvements averaged 32% for gym training and 28% for home workouts across all major movement patterns. The gym advantage in absolute strength primarily benefits advanced powerlifters and strength athletes, while most fitness enthusiasts achieve sufficient strength development through either approach.
Q4: What were the actual body composition changes after six months?
The gym training phase produced 14.2 pounds of lean muscle gain with 3.8 pounds of fat loss, resulting in net 10.4 pounds of weight gain and body fat percentage dropping from 16.5% to 13.2%. The home training phase delivered 13.1 pounds of muscle growth with 4.2 pounds of fat reduction, creating 8.9 pounds net weight increase and body fat declining to 13.8%. Both approaches achieved significant body recomposition though gym training showed slight advantages in absolute muscle gain while home training produced marginally better fat loss results. The combined six-month transformation achieved 23 pounds total muscle gain with body fat percentage decreasing from 16.5% to 15.2%, exceeding typical natural transformation rates.
Q5: How did training consistency differ between gym and home workouts?
Home training achieved 96% workout completion rate (115 of 120 planned sessions) compared to 87% for gym training (104 of 120 sessions), with missed gym workouts primarily attributed to travel time, weather conditions, and facility closures during holidays. The convenience factor of home training eliminated commute time and scheduling conflicts that occasionally prevented gym attendance, though gym environment provided motivational benefits from surrounding exercisers and professional atmosphere that some individuals require for training intensity. This consistency advantage proved crucial as adherence ultimately determines results more than theoretical program superiority, suggesting home training provides better long-term sustainability for busy individuals.
Q6: Which approach better fits busy schedules and time constraints?
Home workouts dramatically reduce total time commitment by eliminating 20-40 minutes of daily commute time to commercial gyms, enabling 45-minute effective training sessions compared to 90-120 minutes including gym travel. The testing revealed home training averaging 52 minutes per session versus 98 minutes total time commitment for gym workouts including transportation. However, gym training provided mental separation from home environment that some individuals value for focus and stress relief beyond pure time efficiency considerations. The 46 minutes daily time savings from home training accumulated to approximately 12 hours monthly that could support meal preparation, additional sleep, or family time all contributing to overall health and fitness outcomes.
Q7: What limitations did home training encounter during the transformation?
Home training faced progressive overload limitations once bodyweight exercises became too easy, requiring creative solutions including weighted vests, resistance bands, and tempo manipulations to continue challenging muscles adequately. The lack of specialized equipment like cable machines, leg press apparatus, and heavy barbells restricted certain exercise variations and maximum load capacity. Space constraints in typical home environments limited exercise selection compared to commercial gym floor space, though creative equipment arrangement and outdoor options partially addressed these limitations. Advanced lifters pursuing maximum strength development eventually require heavy barbell loading exceeding home equipment capacity, though this limitation affects only small percentage of general fitness population.
Q8: How did motivation and mental aspects compare between training locations?
Gym environment provided external motivation through surrounding exercisers, professional atmosphere, and dedicated fitness space creating psychological separation from home responsibilities. However, home training eliminated intimidation factors that prevent some individuals from joining gyms, reduced social anxiety during workouts, and enabled private training sessions without self-consciousness. The testing subject reported feeling equally motivated in both environments after initial adaptation periods, though individual personality types strongly influence location preference for optimal psychological engagement. Extroverts often thrive in gym social environments while introverts may prefer private home training, suggesting personality assessment should guide location decisions.
Q9: Which approach is recommended for beginners starting fitness journeys?
Home training offers superior entry point for beginners through lower financial barriers, private learning environment reducing intimidation, and flexibility accommodating inconsistent early schedules during habit formation. The testing demonstrated that fundamental strength and technique development occurs equally well at home or gym, with beginners benefiting from mastering bodyweight movement patterns before progressing to heavy external loads. However, complete beginners may benefit from initial gym personal training sessions establishing proper form before transitioning to independent home training. The lower financial commitment of home equipment also reduces financial pressure that sometimes causes beginners to abandon expensive gym memberships after motivation declines.
Q10: What is the final recommendation based on six-month results?
Both approaches deliver excellent body transformation results when training intensity, nutrition, and consistency remain optimized, with gym training showing marginal advantages for maximum muscle growth while home training excels in convenience, cost-effectiveness, and schedule flexibility. The ideal solution for many individuals involves hybrid approaches using home training for maintenance and convenience with occasional gym access for specialized equipment and variety. Individual circumstances including budget, schedule constraints, motivation style, and specific goals should determine optimal training location rather than assuming either approach provides universally superior results. The six-month testing proved that training location matters far less than consistent execution of fundamental principles including progressive overload, adequate nutrition, and sufficient recovery.
Articles related:
Tags
📧 Get More Articles Like This
Subscribe to receive product reviews and buying guides in your inbox!
We respect your privacy. Unsubscribe at any time.